Aquifer
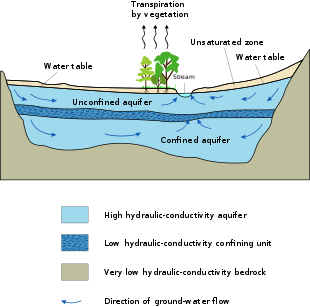
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , rock fractures or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ). Groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer, pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer.
Page Revisions
| Year | Metadata | Sections | Top Words | First Paragraph |
| 2018 |
98058 characters 15 sections 38 paragraphs 10 images 315 internal links 31 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.506 aquifers 0.471 water 0.192 unconfined 0.180 confining 0.160 aquitard 0.140 irrigation 0.138 confined 0.137 groundwater 0.134 freshwater 0.110 aquiclude 0.100 hydraulic 0.099 recharge 0.094 capillary 0.093 wells 0.091 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , rock fractures or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ). Groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer, pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2017 |
97550 characters 15 sections 37 paragraphs 10 images 317 internal links 30 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.511 aquifers 0.466 unconfined 0.198 water 0.190 confining 0.158 confined 0.147 aquitard 0.139 irrigation 0.137 groundwater 0.133 freshwater 0.109 aquiclude 0.099 hydraulic 0.098 recharge 0.093 capillary 0.092 wells 0.090 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , rock fractures or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer, pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2016 |
97232 characters 15 sections 37 paragraphs 10 images 317 internal links 28 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.511 aquifers 0.466 unconfined 0.198 water 0.190 confining 0.158 confined 0.147 aquitard 0.139 irrigation 0.137 groundwater 0.132 freshwater 0.109 aquiclude 0.099 hydraulic 0.098 recharge 0.093 capillary 0.092 wells 0.090 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , rock fractures or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer, pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2015 |
96159 characters 15 sections 37 paragraphs 9 images 315 internal links 29 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.511 aquifers 0.466 unconfined 0.198 water 0.190 confining 0.158 confined 0.147 aquitard 0.139 irrigation 0.137 groundwater 0.132 freshwater 0.109 aquiclude 0.099 hydraulic 0.098 recharge 0.093 capillary 0.092 wells 0.090 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , rock fractures or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer, pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2014 |
93843 characters 16 sections 37 paragraphs 9 images 310 internal links 26 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.538 aquifers 0.453 unconfined 0.197 water 0.196 groundwater 0.139 aquitard 0.138 irrigation 0.136 confined 0.124 confining 0.118 freshwater 0.108 aquiclude 0.098 hydraulic 0.097 capillary 0.091 wells 0.090 basal 0.087 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2013 |
84712 characters 16 sections 38 paragraphs 7 images 277 internal links 27 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.544 aquifers 0.449 water 0.196 unconfined 0.195 groundwater 0.138 aquitard 0.137 irrigation 0.135 confined 0.123 confining 0.117 freshwater 0.107 aquiclude 0.098 hydraulic 0.097 capillary 0.091 wells 0.089 basal 0.086 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2012 |
52005 characters 15 sections 36 paragraphs 3 images 117 internal links 21 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.548 aquifers 0.435 unconfined 0.212 water 0.181 aquitard 0.149 confined 0.133 irrigation 0.132 confining 0.127 groundwater 0.125 aquiclude 0.106 hydraulic 0.105 freshwater 0.104 capillary 0.099 wells 0.097 saltwater 0.096 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2011 |
51631 characters 16 sections 33 paragraphs 3 images 127 internal links 19 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations 4. Human dependence on groundwater |
aquifer 0.563 aquifers 0.402 unconfined 0.218 water 0.188 aquitard 0.153 confined 0.137 confining 0.131 irrigation 0.121 groundwater 0.120 aquiclude 0.109 hydraulic 0.108 freshwater 0.106 capillary 0.101 wells 0.100 saltwater 0.098 |
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , or silt ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2010 |
48514 characters 15 sections 32 paragraphs 3 images 114 internal links 17 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.550 aquifers 0.409 unconfined 0.222 water 0.181 aquitard 0.155 confined 0.139 confining 0.133 irrigation 0.123 groundwater 0.122 aquiclude 0.111 hydraulic 0.110 freshwater 0.108 capillary 0.103 wells 0.101 saltwater 0.100 |
An aquifer is a wet underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include aquitard , which is a bed of low permeability along an aquifer, [1] and aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. If the impermeable area overlies the aquifer pressure could cause it to become a confined aquifer. |
| 2009 |
48751 characters 16 sections 27 paragraphs 4 images 121 internal links 20 external links |
3. Groundwater in rock formations |
aquifer 0.516 aquifers 0.428 unconfined 0.232 water 0.187 aquitard 0.163 confining 0.139 confined 0.133 irrigation 0.128 groundwater 0.119 aquiclude 0.116 hydraulic 0.115 freshwater 0.113 capillary 0.108 saltwater 0.105 unsaturated 0.098 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include: an aquitard , which is an impermeable layer along an aquifer, and an aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area underlying or overlying an aquifer. The surface of saturated material in an aquifer is known as the water table . |
| 2008 |
40972 characters 14 sections 24 paragraphs 2 images 113 internal links 11 external links |
aquifer 0.490 aquifers 0.436 unconfined 0.292 aquitard 0.195 water 0.190 aquiclude 0.146 confining 0.146 confined 0.139 freshwater 0.119 groundwater 0.115 capillary 0.113 saltwater 0.110 table 0.109 unsaturated 0.103 recharge 0.100 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include: an aquitard , which is an impermeable layer along an aquifer, and an aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area beneath an aquifer. The surface of saturated material in an aquifer is known as the water table . |
|
| 2007 |
35786 characters 13 sections 24 paragraphs 2 images 102 internal links 9 external links |
aquifer 0.480 aquifers 0.438 unconfined 0.293 aquitard 0.220 water 0.191 aquiclude 0.147 confining 0.147 confined 0.140 freshwater 0.119 groundwater 0.115 capillary 0.113 saltwater 0.110 unsaturated 0.103 recharge 0.100 table 0.100 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . Related terms include: an aquitard , which is an impermeable layer along an aquifer, and an aquiclude (or aquifuge ), which is a solid, impermeable area beneath an aquifer. |
|
| 2006 |
27625 characters 11 sections 19 paragraphs 1 images 79 internal links 5 external links |
aquifer 0.466 aquifers 0.447 unconfined 0.331 water 0.196 aquitard 0.181 confining 0.150 capillary 0.140 confined 0.137 unsaturated 0.127 recharge 0.123 phreatic 0.121 aquiclude 0.120 table 0.110 pressure 0.109 groundwater 0.095 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water well . The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . |
|
| 2005 |
23984 characters 8 sections 19 paragraphs 1 images 68 internal links 3 external links |
aquifer 0.471 aquifers 0.467 unconfined 0.304 water 0.194 confining 0.152 recharge 0.142 capillary 0.141 confined 0.139 unsaturated 0.129 aquiclude 0.122 aquitard 0.122 pressure 0.110 table 0.099 phreatic 0.098 silt 0.098 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock, or unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) from which groundwater can be usefully extracted using a water_well . A common misconception is that groundwater exists in underground rivers (e.g. caves where water flows freely underground), while the truth is that the pore spaces of rocks in the subsurface are simply saturated with water, which can be pumped out and used for agricultural, industrial or municipal uses. The study of water flow in aquifers and the characterization of aquifers is called hydrogeology . |
|
| 2004 |
7811 characters 1 sections 9 paragraphs 0 images 38 internal links 1 external links |
aquifer 0.556 aquifers 0.435 recharge 0.265 confining 0.227 confined 0.194 water 0.141 silt 0.137 groundwater 0.134 ogallala 0.113 unconsolidated 0.113 gravel 0.107 saltwater 0.102 fresh 0.099 meteoric 0.088 infiltration 0.088 |
An aquifer is an underground layer of water -bearing permeable rock , or permeable mixtures of unconsolidated materials ( gravel , sand , silt , or clay ) (see also groundwater ). Some productive aquifers are in fractured rock ( carbonate rock , basalt , or sandstone ). |
|
| 2003 |
3226 characters 1 sections 5 paragraphs 0 images 11 internal links 0 external links |
aquifers 0.543 aquifer 0.410 water 0.173 gravel 0.167 coastal 0.162 recharge 0.155 wells 0.151 ogallala 0.133 capping 0.133 riparian 0.133 topmost 0.120 corridors 0.120 fresh 0.115 areas 0.110 reversal 0.102 |
An aquifer is a layer of water-bearing permeable rock , sand, or gravel capable of providing significant amounts of water (see also groundwater ). The upper boundary of the topmost aquifer is known as the water table . Some areas have several aquifers, each capped on top by an impervious layer. If the recharge area is elevated higher that the capping layer, the water may be under considerable pressure, and flowing or Artesian wells may be likely. Most land areas on Earth have some form of aquifer underlying them, though often at significant depth. Aquifers in coastal regions do not necessarily contain fresh water , especially when they have been pumped at rates exceeding the input of fresh water from the recharge area. Such reversal of normal flow toward the ocean leads to intrusion of sea water backward into the acquifer, which is a serious problem in many coastal areas. |
|
| 2002 |
997 characters 0 sections 1 paragraphs 0 images 2 internal links 0 external links |
aquifer 0.586 permeable 0.402 gravel 0.357 bearing 0.242 table 0.231 providing 0.207 capable 0.205 water 0.202 boundary 0.191 sand 0.157 amounts 0.146 upper 0.132 layer 0.131 rock 0.114 |
An aquifer is a layer of water-bearing permeable rock, sand, or gravel capable of providing significant amounts of water. The upper boundary of an aquifer is known as the water table . |